как узнать версию gradle в idea
ПРОграммирование под Android
Страницы
26 марта 2015 г.
Настройка IntelliJ IDEA и Gradle
Сегодня обновил IntelliJ IEDEA с версии 14.0.3 на версию 14.1. И после этого началась …
IntelliJ IDEA захотела заново скачать дистриб Gradle, хотя он уже был на компе, от предыдущей версии. И ладно бы начала скачивать новую версию, так нет же, качает старую, такую же как уже есть.
На этом мое терпение лопнуло и я решил разобраться с Gradle раз и на всегда!
Идем на сайт Gradle и качаем дистриб. На данный момент это версия 2.3, а IDEA качала с этого же сайта более старую версию 2.2.1
Дистриб из себя представляет просто архив gradle-2.3-all.zip. Я его разархивировал в C:\gradle-2.3
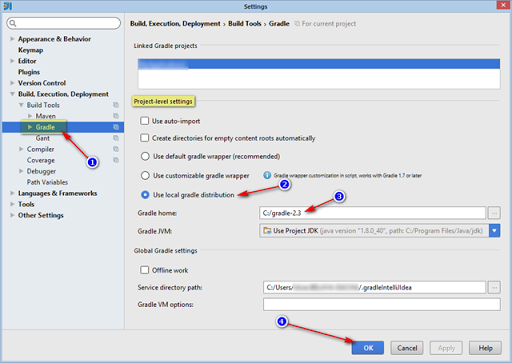
Далее идем в настройки IntelliJ IDEA и делаем раз, два, три, четыре…
Теперь, чтобы старые файлы Gradle не занимали место, все их можно удалить из каталога
C:\Users\ \.gradleIntelliJIdea
Хотя это я у себя настроил такой каталог, у вас может быть просто .gradle
Но и после этого Gradle еще сильно тормозил собирая проекты. Чтобы придать ему ускорение, надо немного изменить файл настроек gradle.properties в проекте
После всех этих манипуляций, при попытку установить (запустить) приложение на виртуальное устройство может выскочить ошибка
INSTALL_FAILED_UID_CHANGED
Это можно вылечить подправив параметр applicationId в файлике проекта
Про эту ошибочку можно еще почитать тут и чтобы понять что происходит тут.
Вкратце это произошло потому, что приложение не корректно было удалено и оставило свою папку в каталоге /data/data
Так же эту проблему можно решить удалив каталог программы с устройства через adb shell.
Утилитка adb живет по пути C:\android-sdk-windows\platform-tools ну по крайней мере у меня, у вас может быть другой путь. Запускаем ее в командной строке с параметром devices
Далее даем команду adb remount, чтобы смонтировать файловую систему устройства с правами на запись.
Далее запускаем shell на устройстве
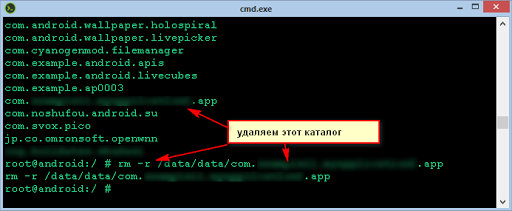
И далее смотрим содержимое каталога /data/data командой ls /data/data
Вывод у этой команды достаточно длинный, так как выводятся все приложения установленные на устройстве
Ну и далее удаляем каталог программы, которая не может установиться по запуску из IntelliJ IDEA
На заметку некоторые adb команды
adb devices – список устройств которые уже прикреплены к компьютеру
adb install
– позволяет установить приложение на устройство
adb remount – размонтирует систему в режим записи – позволяет менять системные файлы на устройстве используя ADB
adb push – позволяет загружать файлы в файловую систему устройства
adb pull – позволяет скачивать файлы с файловой системы устройства
adb logcat – начинает дампить отладочную информацию с устройства в консоль – полезно для отладки приложений
adb shell – бросает вас в базовые shell команды linux’а без параметров, или позволяет непосредственно запускать команды
Хотя там, почему-то далеко не все команды adb перечислены.
Полную справку по командам можно получить через сам adb. Просто дав эту команду безе параметров.
Gradle
IntelliJ IDEA supports a fully-functional integration with Gradle that helps you automate your building process. You can easily create a new Gradle project, open and sync an existing one, work with several linked projects simultaneously, and manage them.
You can also create a Gradle project and store it in the WSL environment or open it from the WSL file system. For more information, refer to the WSL section.
Create a new Gradle project
Launch the New Project wizard. If no project is currently opened in IntelliJ IDEA, click New Project on the welcome screen. Otherwise, select File | New | Project from the main menu.
Select Gradle from the options on the left.
If you don’t have a JDK on your machine, IntelliJ IDEA can quickly download the JDK for you.
The Gradle project sync will wait until the JDK is downloaded.
For more information on Maven coordinates, see Maven naming conventions.
Create a Java EE project with Gradle as a build tool
Launch the New Project wizard. If no project is currently opened in IntelliJ IDEA, click New Project on the welcome screen. Otherwise, select File | New | Project from the main menu.
Select Java Enterprise from the options on the left.
IntelliJ IDEA creates a Gradle project with the dedicated Gradle tool window and adds necessary dependencies.
For the more detailed information, refer to Tutorial: Your first Java EE application.
Open an existing Gradle project
If you have the offline mode enabled in your project, the opening or re-importing of the project might fail. To fix the issue, disable the offline mode and re-import your project.
If you have some custom plugins that require you to import your project from the IntelliJ IDEA model, press Ctrl+Shift+A and search for the Project from Existing Sources action.
IntelliJ IDEA opens and syncs the project in the IDE.
If you need to adjust the Gradle settings options, refer to Gradle settings.
Check Gradle JVM and language level
Gradle JVM : when IntelliJ IDEA opens the Gradle project, it checks the gradle.properties file for the appropriate JVM version specified in org.gradle.java.home and uses it for the project. If it is not specified, then the project SDK is used. Alternatively, you can use the Gradle settings to configure the Gradle JVM.
Link a Gradle project to an IntelliJ IDEA project
You can have multiple Gradle projects inside one IntelliJ IDEA project. It might be helpful if you keep parts of code in different projects, have some legacy projects on which you need to work, have Gradle composite build or work with microservices. You can link such projects in IntelliJ IDEA and manage them simultaneously.
When you open a Gradle project, the link of the project is established automatically and the Gradle tool window is enabled.
If an IntelliJ IDEA project is not linked to a Gradle project, then the Gradle tool window is disabled. In this case, IntelliJ IDEA displays a message with a link that quickly lets you reimport your Gradle project and enable the Gradle tool window. If the Gradle tool window is active, then you have at least one Gradle project linked.
Open the Gradle tool window.
The project is linked. The Gradle tool window shows the toolbar and a tree view of Gradle entities.
Add a new Gradle module to an existing Gradle project
You can add a Gradle module to a project in which you are already working.
In a project, from the main menu, select File| New | Module to open the New Module wizard.
Convert a regular project into a Gradle project
Open your project in IntelliJ IDEA.
As soon as you create a build.gradle file, IntelliJ IDEA recognizes the Gradle build script and displays a notification suggesting to load the project as Gradle. After you load the project, IntelliJ IDEA enables the Gradle tool window.
We also recommend that you add the settings.gradle file to your project and add rootProject.name = ‘projectName’ to it. Where ‘projectName’ would be the name of your project.
Access the Gradle settings
Use the Gradle settings to configure the build and run actions for each linked Gradle project, a Gradle version, importing of the project’s changes, and so on.
On the Gradle settings page, configure the available options and click OK to save the changes.
Configure a Gradle version for a project
IntelliJ IDEA lets you use different options to configure a Gradle version for your Gradle project. You can use the default Gradle wrapper, use a Gradle wrapper as a task, or configure a local Gradle distribution.
In this case you delegate the update of Gradle versions to Gradle and get an automatic Gradle download for the build. This option also lets you build with a precise Gradle version. The Gradle version is saved in the gradle-wrapper.properties file in the gradle directory of your project and helps you eliminate any Gradle version problems.
If you used the default Gradle wrapper option and then switched to the Gradle wrapper task configuration, changes you made in the task automatically update during the project import.
Specified location : select this option if you want to manually download and use a specific Gradle version. Specify the location of your Gradle installation and JVM under which IntelliJ IDEA will run Gradle when you import the specified Gradle project and when you execute its tasks.
Click OK to save the changes.
Add VM options for the Gradle project
You can specify VM options for your Gradle project using the gradle.properties file.
Create or open your Gradle project.
Open the created file in the editor and add the VM options you need.
For more information, refer to the Gradle documentation.
Gradle projects
IntelliJ IDEA lets you manage Gradle projects. You can link, ignore projects, work with profiles, and synchronize changes in Gradle and IntelliJ IDEA projects. You can also configure a Gradle composite build, Gradle source sets, the build and run actions.
Navigate to the build.gradle file
In the Gradle tool window, right-click a linked project.
IntelliJ IDEA navigates to the appropriate Gradle configuration file and the related build.gradle file opens in the editor.
Navigate inside a multi-module project
IntelliJ IDEA supports a navigation to subprojects inside the parent build script of a multi-module Gradle project.
Open build.gradle of the parent project.
You can also see the usages of a subprojects with the Alt+F7 and check the results in the Find tool window.
Unlink a linked Gradle project
When you unlink a Gradle project, IntelliJ IDEA removes all relevant modules and content roots, removes the Gradle project from the Gradle tool window and stops its synchronization. It might be helpful if you need to fully remove the previously linked Gradle project from the current IntelliJ IDEA project.
In the Gradle tool window, right-click a linked project.
In the Import Gradle Projects popup, clear the checkbox against the modules if you don’t want to delete the project from the IntelliJ IDEA Project tool window.
Ignore a Gradle project
In the Gradle tool window, right-click the project that you want to ignore.
If you want to activate your Gradle projects or modules, select Unignore Gradle Projects from the context menu.
Orphan modules
Orphan modules are the IDE modules that were removed during the import process in the following cases:
when you manually deleted the modules in the build.gradle file and then re-imported your project.
when you used the Ignore Project action, on a module in the Gradle tool window and then re-imported your project.
In all these cases, IntelliJ IDEA prompts you to restore removed modules.
You can select the ones you want to restore in the Orphan Modules dialog.
Reload a linked Gradle project
When you open a Gradle project the synchronization is done automatically. Also, when IntelliJ IDEA detects any external changes to the build scripts, such as VCS updates or some edits made outside of the IDE, the related projects will be reloaded automatically.
If you need, you can manually trigger the synchronization of your project.
In the Gradle tool window, right-click a linked project.
On invoking this action, IntelliJ IDEA parses the project structure in the Gradle tool window.
IntelliJ IDEA cannot reload just a part of your project, it reloads the whole project including modules and dependencies.
Configure the auto-reload
Reload changes in the build scripts : this option is selected by default. If you want to disable the auto-reload and manually control the reloading process, unselect this checkbox.
Every time you manually change the Gradle build script in the editor, you need to load the changes. IntelliJ IDEA displays a nofication icon in the right part of the editor suggesting to Load Gradle Changes made to the project ( Ctrl+Shift+O ).
With the Any changes option, IntelliJ IDEA reloads all the changes automatically.
External chages : when you select this option, IntelliJ IDEA automatically reloads the project only after the VCS changes and changes made to the build files outside the IDE.
Configure Gradle Composite Build
Before you start configuring your composite build, make sure you have the Gradle version 3.1 or later configured for your project.
You can use the settings.gradle file to include Gradle builds for your Gradle composite build.
Open the settings.gradle file in the editor.
Using the includeBuild command, specify the location of the builds you want to add as dependencies to your project.
You can also use the Gradle tool window to configure the composite build.
Open a Gradle project.
Link other Gradle projects that you want to use for the composite build.
In the Gradle Project Build Composite dialog, select projects that you want to include in your Gradle composite build.
IntelliJ IDEA finds the included Gradle projects and treats them as IntelliJ IDEA modules.
Use Gradle source sets
IntelliJ IDEA lets you use Gradle source sets in resolving Gradle projects. The source set is treated as a module in an IntelliJ IDEA project. You can declare a custom source set and IntelliJ IDEA adds it as a module to the project.
Add a custom source set
Open the gradle.build file in the editor.
Declare a custom source set (In our example, it’s api).
Open the Gradle tool window to see that IntelliJ IDEA added the api compile and runtime configurations. 
From the main menu, select File | Project Structure Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S to open the project structure. Notice that all source sets are represented as separate modules that are grouped into a single module. If you click the test module and select the Dependencies tab, you will see a list of dependencies for the source set.
Use source sets for custom tests
You can add custom tests and run them separately from the main ones using a source set feature.
In the list that opens, double-click the integrationTest to run it.
Add package prefixes in the Gradle project
If you use package prefixes in your Gradle project, specify them in the build.gradle file. That way, everything is saved when you reimport your project.
Open the build.gradle file.
Add the following plugin to support package prefixes:
Add the package prefixes. For example, you have the following set of source sets:
Reimport your changes or use the auto-import.
Specify IDE-specific settings in the build.gradle file
Using the gradle-idea-ext plugin, you can describe project settings such as project encodings, and the encoding for properties files inside the build.gradle file.
Open the build.gradle file.
Add the following plugin to support the encodings configuration:
is a string constant indicating that system default encoding settings will be used.
Reimport your changes or use the auto-import.
Use buildSrc
If you have a large Gradle script that includes several Java, Groovy, or Kotlin classes, you can move such classes to the buildSrc directory and refer to them from your main Gradle script. In this case you ensure the readability of the build.gradle file.
Open your main build.gradle file in the editor and move the classes you need to the main subdirectory of the buildSrc directory.
Run your task from your project’s build.gradle file.
You can use the Rename Shift+F6 refactoring if you need to change the name of a class to which you refer in the Gradle script. IntelliJ IDEA applies changes to all the references.
Configure the build and run actions
By default, IntelliJ IDEA uses Gradle for building and running projects.
When you build a project ( Build | Build Project ), IntelliJ IDEA invokes the corresponding tasks using Gradle. Gradle also executes the Run and Debug actions from the Run menu. HotSwap is also gets triggered and the classes are reloaded during a debugging process.
If you have linked projects, you can configure how to build each linked project.
If you use the annotationProcessors in your project, we recommend that you delegate run and build actions to Gradle, so the annotation processor will be correctly enabled in your project.
On the Gradle settings page, in the Gradle Projects section, select a Gradle project you need.
In the Build and run using list, select the appropriate option and click OK to save the changes.
If you want to use IntelliJ IDEA for building a Gradle project, you need to explicitly specify so.
Delegate a build to IntelliJ IDEA
It might be helpful to use IntelliJ IDEA for building a pure Java or Kotlin project. It could speed up the building process since IntelliJ IDEA supports the incremental build. Yet, keep in mind that the IntelliJ IDEA compiler does not support some parts of the Gradle project build processing and might cause problems in building your project correctly.
Now if you build your Gradle project, it will be built with IntelliJ IDEA.
Как определить Gradle дома в IDEA?
ОТВЕТЫ
Ответ 1
Затем запустите его с:
Ответ 2
Установленный на Mac через Homebrew путь
так как первая выживет при обновлении версии.
Ответ 3
Если вы установили gradle с доморощенным, то путь следующий:
Ответ 4
Если вы используете IntelliJ, просто выполните следующее.
Ответ 5
Это то, что помогло мне решить проблему отсутствия установки Gradle для IDEA при импорте проекта Gradle.
A. Упаковщик по умолчанию (рекомендуется)
Если вы можете, выберите этот рекомендуемый вариант. Если он неактивен, см. Опцию C, которая затем должна установить значение по умолчанию для всех последующих проектов.
B. Конфигурация задачи Gradle ‘Wrapper’
Если вы хотите, чтобы IDEA определил вашу версию Gradle из вашего скрипта сборки
(полезно, если вы не хотите делиться сборками Gradle между проектами)
C. Местное распределение Gradle
Это связано с тем, что «libexec должен использоваться другими демонами и системными утилитами, выполняемыми другими программами» (например, IDEA). Пожалуйста, смотрите https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/312146/what-is-the-purpose-of-usr-libexec
Ответ 6
Я написал свою статью с инструкцией на случай, если кто-то столкнется с такой же проблемой.
Ответ 7
На Mac это в идеале должно быть по адресу: /Applications/Android Studio.app/Contents/gradle/gradle-2.14.1
(Замените строку версии последней)
Ответ 8
\Android студия \Gradle не работает для меня.
И «Default gradle wrapper» не был настроен при импорте (клонировании) проекта из bitbucket
Ответ 9
AFAIK GRADLE_HOME не GRADLE_USER_HOME (см. gradle установка http://www.gradle.org/installation).
С другой стороны, я немного играл с поддержкой gradle в Idea 13 Cardea, и я думаю, что дом gradle не будет автоматически обнаружен Idea. Если это так, вы можете указать проблему в youtrack.
Кроме того, если вы используете gradle 1.6+, вы можете использовать поддержку Graldle для установки сборки и обертки. Я думаю, что идея автоматически обнаруживает проект gradle на основе обертки.
Примечание. Поддерживаемые типы библиотек: basic, maven, java
Ответ 10
Если вы используете MacPorts, путь
Ответ 11
Мне пришлось настроить Project SDK, прежде чем выбрать путь Gradle. После того, как это было установлено правильно, мне пришлось выбрать «Использовать упаковщик Gradle по умолчанию (рекомендуется) в диалоговом окне» Импортировать проект из Gradle «.
Все еще работает, если я удаляю Gradle, используя Brew:
Ответ 12
У меня были некоторые странные ошибки, когда он не мог найти мой класс, мне пришлось щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по моей папке src (был красным), чтобы «Сделать каталог как» → Корень исходной папки
Ответ 13
Вот где находится мой укромный дом (Arch Linux):
Ответ 14
Предпочтение от поиска IDEA для gradle и установите gradle home, как указано выше. Он должен работать
Ответ 15
Нажмите New → Project из существующих источников → Import gradle project.
Тогда идея распознается автоматически.
Ответ 16
Я не мог заставить его принять мой выбор Gradle JVM, пока я не удалил сломанный JDK
Это окно из меню Файл → Другие настройки → Структура для новых проектов.
У меня была красная запись 1.8 JDK SDK здесь, когда я удалил эту ошибку Gradle JVM исчезла